Broken links are detrimental to your website’s performance, user experience, and search engine optimization (SEO). They lead to dead ends for users, result in crawling issues for search engines, and can significantly harm your site’s credibility and rankings. SEMrush offers a powerful and comprehensive solution to identify and fix these broken links through its Site Audit tool. This guide will walk you through the entire process of finding and fixing broken links using SEMrush, from setting up your audit to implementing preventive measures.
Step 1: Accessing the Site Audit Tool
The first step in identifying broken links on your website is to initiate a Site Audit within SEMrush. To do this, log in to your SEMrush account. On the dashboard, you’ll find various tools and options for managing your website’s SEO. Navigate to the ‘Site Audit’ tool under the Projects section.
- Creating a New Project: If you haven’t already set up a project for your website, you’ll need to create one. Click on the ‘Add New Project’ button, enter your website’s domain, and name the project for easy identification.
- Setting Up Your Audit: Once the project is created, you’ll be directed to the Site Audit settings. Here, you can configure how you want SEMrush to crawl your website, focusing on finding broken links across your entire site.
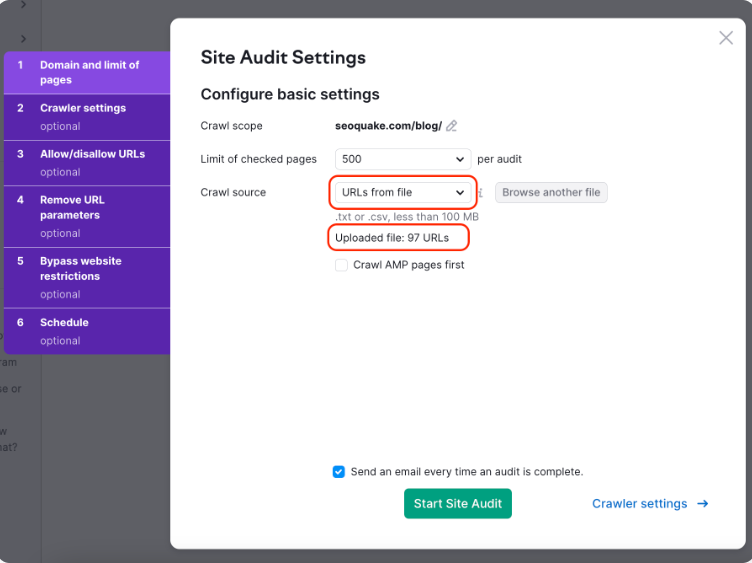
Step 2: Customizing the Audit Parameters
SEMrush allows you to tailor the Site Audit to meet your specific needs. This customization ensures that you get the most relevant and comprehensive data, particularly regarding broken links.
- Scope of the Audit: Decide whether you want SEMrush to crawl the entire website or specific sections. For a thorough check of broken links, it’s recommended to audit the entire site. This ensures that no broken link goes unnoticed, whether it’s on the homepage or buried deep within the site.
- User Agent Selection: Choose the user agent that SEMrush will use to crawl your website. The user agent could mimic a search engine crawler (like Googlebot) or a desktop/mobile browser. This setting is important because different user agents might experience different link behaviors, especially in dynamically served content.
- Crawl Depth: Determine how deep SEMrush should crawl into your website. A deeper crawl will check more pages and links but will take longer. For most websites, a depth of 3 to 5 levels is sufficient to capture the majority of links.
- Excluding Specific Sections: You might have certain areas of your website that you don’t want to be crawled, such as staging sites or archives. Use the ‘Exclude URLs’ option to prevent SEMrush from auditing these sections.
Step 3: Executing the Crawl
After you’ve configured your settings, you’re ready to run the audit. Click the ‘Start Audit’ button, and SEMrush will begin crawling your site. Depending on the size of your website, this process could take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
- Real-Time Progress: SEMrush provides real-time updates on the audit’s progress. You can monitor the number of pages crawled, issues detected, and the estimated time remaining.
- Audit Completion: Once the audit is complete, SEMrush generates a comprehensive report. This report will list all the issues found on your website, with broken links prominently displayed due to their critical nature.
Step 4: Understanding and Navigating the Report
The Site Audit report is your roadmap to identifying and fixing broken links. SEMrush categorizes all issues found into three levels: errors, warnings, and notices. Broken links are typically categorized under errors because they are a high-priority issue that needs immediate attention.
- Identifying Broken Links:
- Internal Broken Links: These are links within your website that point to other pages on your site but no longer work. For example, this could happen if a page has been deleted or its URL has changed without a proper redirect in place.
- External Broken Links: These are links on your website that point to external websites or resources that are no longer available. This could be due to the external site removing the page or changing its URL.
- Report Details:
- Page Location: The report will tell you exactly which page on your site contains the broken link. This is crucial for quick navigation and fixes.
- Target URL: SEMrush will provide the URL of the broken link, so you can assess why it’s broken—whether the target page has been moved, deleted, or if there’s a typographical error in the link.
- Understanding Metrics and Status Codes:
- HTTP Status Codes: The report will include the HTTP status codes associated with the broken links. Common codes include 404 (Not Found), 500 (Server Error), and 403 (Forbidden). These codes can give you insight into why the link is broken.
- Number of Affected Pages: SEMrush also provides metrics on how many pages are affected by each broken link. This helps in understanding the scale of the problem.
Step 5: Prioritizing and Fixing Broken Links
With the report in hand, you can now start fixing the broken links. Prioritize your actions based on the impact of each broken link.
- Prioritization:
- High-Traffic Pages: Start by fixing broken links on pages that receive the most traffic. These pages are crucial for user experience and SEO.
- SEO Critical Pages: Pages that are key to your SEO strategy, such as landing pages and blog posts, should also be prioritized. Broken links on these pages can have a significant impact on your rankings.
- Correcting Broken Links:
- Internal Links: For internal broken links, check if the target page still exists but has a new URL. If so, update the link to reflect the correct URL. If the page no longer exists and there’s no suitable replacement, consider removing the link.
- External Links: For external broken links, determine if the target page has been moved or deleted. You can replace the link with an alternative resource or remove it if no suitable replacement is available.
- Implementing Redirects:
- 301 Redirects: If a page has been permanently moved, setting up a 301 redirect ensures that users and search engines are redirected to the new URL. This is especially important for maintaining SEO value.
Step 6: Regular Monitoring and Site Maintenance
Fixing broken links is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing maintenance to ensure your website remains in good health. SEMrush makes it easy to monitor your site for broken links regularly.
- Schedule Regular Audits: SEMrush allows you to set up automated audits that run at regular intervals. Weekly or monthly audits are recommended, depending on how frequently your site’s content is updated.
- Monitoring New Content: As you add new pages and content to your website, ensure that links are working correctly. Implement a checklist for link verification before publishing any new page.
- Use of Plugins and Extensions: For websites running on platforms like WordPress, there are plugins available that can help monitor and fix broken links in real-time. Integrating these with SEMrush audits provides an additional layer of protection.
- Setting Up Alerts: SEMrush can send you notifications if new issues are detected between scheduled audits. This proactive approach helps you address problems before they escalate.
Step 7: Troubleshooting and Best Practices
While SEMrush makes it straightforward to find and fix broken links, you may encounter certain challenges during the process.
- Identifying Complex Issues: Sometimes, a broken link might not be easily fixable due to complex URL structures or issues with dynamic content. In such cases, further investigation into your site’s architecture may be required.
- Handling a Large Volume of Broken Links: If your site has hundreds or thousands of broken links, addressing them all can seem daunting. Prioritize by impact and consider breaking the task into smaller, manageable parts.
- Working with External Partners: For external links, if the broken link points to a partner or affiliate site, reach out to them to update the link on their end. This can help in maintaining the integrity of your site’s content.
Conclusion
Maintaining a website free of broken links is essential for ensuring a positive user experience and robust SEO performance. SEMrush’s Site Audit tool provides a comprehensive, user-friendly solution for identifying and fixing these issues. By following the detailed steps in this guide, you can efficiently manage and rectify broken links on your site, helping you maintain your website’s health and improve your search engine rankings.